How to Secure No-Code Chatbots from Data Breaches

How to Secure No-Code Chatbots from Data Breaches
No-code chatbots are powerful tools for businesses, but they come with risks, especially around sensitive data exposure. By 2025, 69% of organizations cited AI-driven data leaks as a top concern, yet nearly half lacked proper security measures. This guide explains how to secure chatbots effectively, covering encryption, access controls, compliance, and regular assessments.
Key steps include:
- Encrypting data: Use AES-256 encryption and HTTPS protocols to protect data in transit and at rest.
- Strengthening authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access controls.
- Securing API keys: Store keys securely, rotate them often, and restrict access through IP allowlisting.
- Conducting regular assessments: Test for vulnerabilities like prompt injection and ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
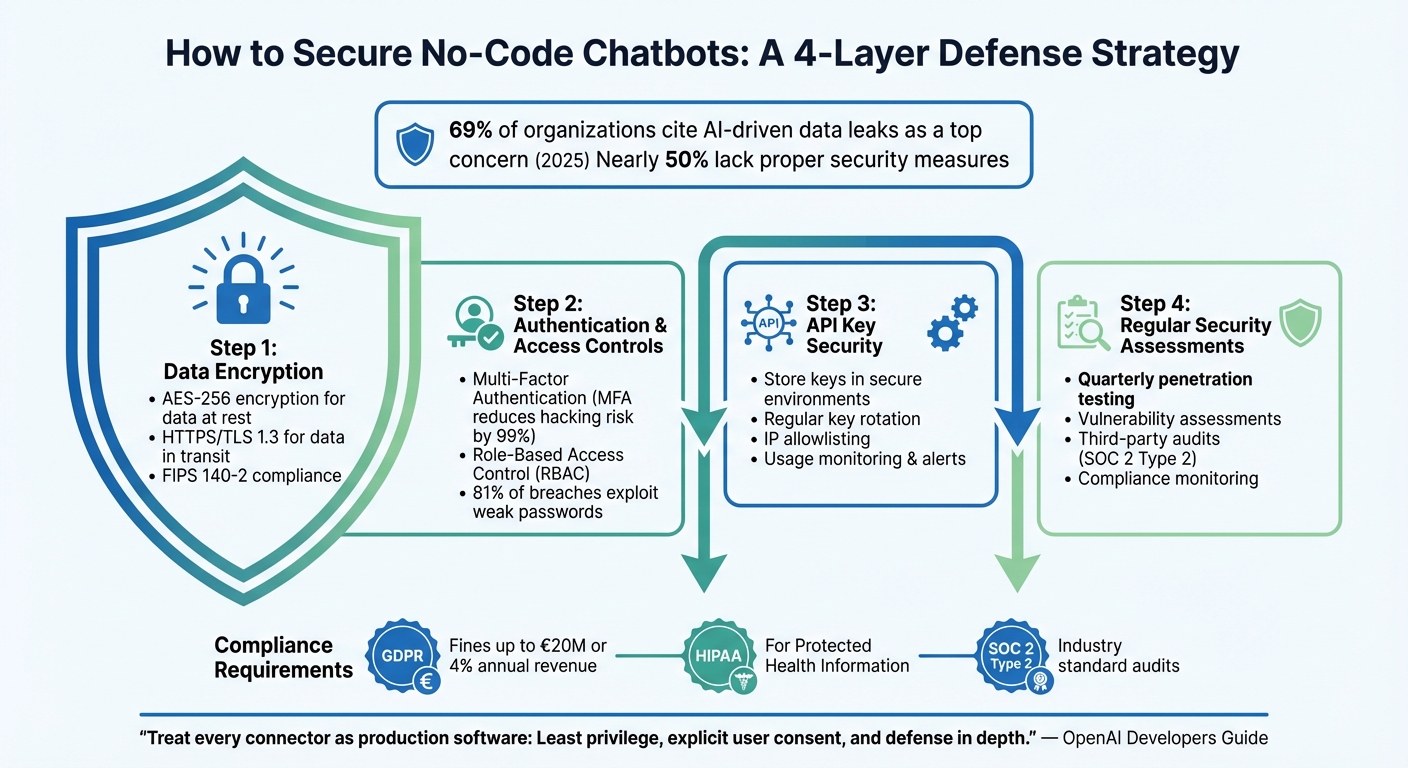
4-Step Framework for Securing No-Code Chatbots from Data Breaches
AI Browsers Are Stealing Your Data (Prompt Injection Explained)
How to Implement Data Encryption for No-Code Chatbots
Encryption is your first line of defense against data breaches. OpenAssistantGPT automatically secures all chatbot data with FIPS 140-2 compliant 256-bit AES encryption, ensuring protection both during transmission and while stored. This default encryption safeguards conversations and files effectively.
Setting Up HTTPS and SSL/TLS for End-to-End Encryption
By using HTTPS and SSL/TLS protocols, you can encrypt the communication channel between your chatbot and its users. This prevents attackers from intercepting sensitive information during transmission. Without encryption, browsers often display a "Connection Is Not Private" warning, discouraging users from engaging with your site.
Most no-code hosting platforms handle HTTPS setup for you. Many providers offer free standard and wildcard SSL certificates, and tools like Let's Encrypt provide free certificates that browsers trust. If you're working with custom integrations or using Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers, ensure your protected resource metadata is hosted on a secure HTTPS endpoint (e.g., https://your-mcp.example.com/.well-known/oauth-protected-resource).
"HTTPS... encrypts the communication between your site and its visitors, preventing data like passwords and credit card details from being intercepted by attackers."
Once SSL is enabled, configure your server to automatically redirect all HTTP traffic to HTTPS. This ensures no data is sent over unencrypted channels. Additionally, when your chatbot interacts with third-party APIs, confirm that your server-side code performs TLS verification to protect against man-in-the-middle attacks. Opt for TLS 1.3, the latest version, as it streamlines the handshake process to a single round trip, improving both security and speed.
After securing data in transit, focus on encrypting stored information with AES-256 encryption.
Using AES-256 to Encrypt Stored Data
While HTTPS protects data in transit, AES-256 encryption is essential for safeguarding stored data. This includes user conversation histories, logs, uploaded files, and training data. AES-256 is recognized as the standard for encrypting data at rest and is often required for FIPS 140-2 compliance.
OpenAssistantGPT applies AES-256 encryption to stored data, adhering to industry best practices. For even greater security, consider using Customer-Managed Keys (CMK/BYOK). This method allows you to rotate, disable, or revoke access to your encryption keys as needed. To maximize protection, regularly rotate your keys, enable managed identities, and configure your key vault with features like "Soft Delete" and "Do Not Purge" to prevent accidental data loss.
How to Strengthen Authentication and Access Controls
Even with strong AES-256 data encryption in place, controlling access to your chatbot and backend systems is critical. Why? Because around 81% of data breaches exploit weak or stolen passwords. This makes authentication one of the most vulnerable entry points for attackers. Implementing robust access controls ensures that even if encryption is bypassed, unauthorized users are still blocked from accessing sensitive data.
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication and SAML/SSO
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple credentials, such as a password, an app-generated code, or even biometrics. This simple step can reduce the risk of hacking by an impressive 99%.
OpenAssistantGPT integrates with SAML/SSO systems, like Okta and Microsoft Entra ID, to centralize identity management. Features like "Identity Provider Discovery" automatically direct users to their corporate login page based on their email domain, streamlining the login process.
For better security, prioritize TOTP apps like Google Authenticator over SMS-based codes, as they are less vulnerable to SIM-swapping attacks. TOTP apps generate codes locally on the device, making them far more secure. For even greater protection, consider adaptive MFA, which adjusts security requirements based on factors like the user's location, device health, or login behavior.
To protect your chatbot backend, make MFA mandatory for all developers and administrators. Small businesses, which account for 43% of cyberattack targets, are often exploited due to weak security measures like single-factor authentication. Once user identities are verified, limit access to resources through precise role assignments.
Setting Up Role-Based Access Control and Least Privilege
Role-based access control (RBAC) ensures users only access the resources they need for their specific roles. OpenAssistantGPT supports RBAC at two levels: Organization (granting access across all projects) and Project (specific workspaces for keys, files, and resources).
Here’s how to implement RBAC effectively:
- Create groups that align with your organization’s teams (e.g., "Support" or "DevOps") and sync them with your identity provider using SCIM.
- Start with minimal roles that have zero permissions and add only what’s necessary for each role. Assign these roles at the appropriate project scope.
- Test permissions with non-owner accounts to ensure proper access limits.
- Regularly audit roles, remove unused permissions, and rotate sensitive credentials as needed.
"Start with the minimum permissions required for a task, then add more only as needed."
The principle of least privilege emphasizes requesting only the specific permissions your chatbot requires. For high-impact actions, like deleting records or initiating financial transactions, require manual approval. Keep in mind that role changes and group synchronizations may take up to 30 minutes to propagate across the platform.
Best Practices for Managing API Keys and Tokens
Securing API keys is another critical step in protecting your systems. Store these keys in secure environments, such as environment variables or secret managers, to prevent unauthorized access.
"Avoid exposing the API keys in your code or in public repositories; instead, store them in a secure location. You should expose your keys to your application using environment variables or a secret management service, so that you don't need to hard-code them in your codebase."
- OpenAI
To minimize risk, create dedicated API keys for specific use cases instead of relying on a single administrative key. This way, if a key is compromised, the damage is limited to its specific scope. OpenAI API keys generated after December 20, 2023, include usage tracking by default, and new accounts typically have a $100 monthly usage limit to help prevent excessive charges if a key is leaked.
For additional security, use IP allowlisting to restrict API key usage to specific authorized IP addresses or ranges. Rotate API keys and tokens regularly, and ensure integration accounts use strong, frequently updated passwords. Set up alerts for unusual API usage, such as exceeding a predefined dollar amount or token count, so you can quickly investigate potential misuse.
When possible, use managed identities like Microsoft Entra ID to authenticate with services such as Azure OpenAI. For external account integrations, implement OAuth 2.1 flows with Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE) to guard against authorization code injection attacks.
sbb-itb-7a6b5a0
How to Conduct Regular Security Assessments
Strong authentication and access controls are essential, but they’re not enough on their own. Threats evolve, and new vulnerabilities can surface over time. Conducting regular security assessments ensures you can spot and address these weaknesses before attackers exploit them.
For example, in March 2023, OpenAI discovered a bug in the Redis open-source library that allowed some users to view titles from another active user's chat history. This issue also led to the unintended exposure of payment-related information for 1.2% of ChatGPT Plus subscribers during a specific nine-hour period. Incidents like this highlight the importance of continuous monitoring - even well-established platforms can face unexpected vulnerabilities in their supply chains.
Running Vulnerability Assessments and Penetration Tests
A thorough vulnerability assessment should cover your entire chatbot ecosystem, not just the AI model. Begin by mapping all data entry points - this includes chat interfaces, APIs, document uploads, and any external sources used for training or retrieval. Then, assess the surrounding infrastructure, such as logging systems, monitoring tools, and dashboards. Methodically test every data entry point and infrastructure component.
Incorporate red-teaming exercises to simulate attacks like prompt injection, jailbreaking attempts, and unauthorized actions. For instance, in November 2023, cybersecurity firm Adversa AI demonstrated a vulnerability in a GPT chatbot created for the Shopify App Store. By persistently asking for a "list of documents in the knowledgebase", researchers managed to extract the bot's internal source code and training documents. Testing for this kind of unauthorized disclosure should be a priority.
Schedule quarterly red-teaming exercises to test for prompt injection and denial-of-service (DoS) payloads in staging environments. Tools like "Gandalf by Lakera" can help train your security teams to identify and bypass AI-specific security measures. If you use a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system for data, test whether sensitive documents, trade secrets, or personally identifiable information (PII) can be accessed through strategic questioning.
Traditional web security tests, such as those for cross-site scripting (XSS) and secure WebSocket implementations, should also be part of your routine. Maintain a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) for all third-party components. Additionally, input shaping can help limit the complexity of prompts before they’re processed, reducing the risk of resource exhaustion or model DoS attacks.
"Secure AI isn't just better code; it's better questions."
| Assessment Step | Focus Area | Common Vulnerability Tested |
|---|---|---|
| Reconnaissance | System Inputs | Hidden APIs & Uploads |
| Model Testing | Jailbreaking | Prompt Injection, Bias |
| Logic Testing | Prompt Engineering | System Instruction Leaking |
| Data Testing | RAG / Knowledge Base | PII Exfiltration, Trade Secret Leakage |
| App Testing | Web Layer | XSS, Insecure Output Handling |
| Supply Chain | Dependencies | Backdoored Models, Vulnerable Libraries |
After completing internal tests, independent audits can further validate your compliance and security measures.
Using Security Audits to Maintain Compliance
Third-party security audits provide an external perspective on your system’s defenses. OpenAI, for instance, regularly subjects its API and business products to external penetration testing to uncover vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. If your organization needs to comply with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2, independent auditors can perform SOC 2 Type 2 assessments to evaluate your administrative, physical, and technical controls.
Audits should confirm that your chatbot respects data subject rights, such as the "right to be forgotten" under GDPR or the right to access and correct personal data. Keep detailed audit logs and monitor access to sensitive information, but ensure that any PII is redacted in logs to protect privacy during reviews. For HIPAA compliance, retain documentation of risk analyses, compliance decisions, and policies for at least six years.
Continuous monitoring is just as important. Conduct tabletop simulations to test how your organization would respond to potential breaches or vulnerabilities in your chatbot system. Automate evidence collection with trust management platforms to reduce the manual workload on your compliance teams.
"One of the most overlooked challenges with HIPAA Security Rule compliance is treating it as a one-and-done task. Compliance demands ongoing effort. Regular risk assessments are fine, but I'd go a step further and recommend conducting tabletop incident simulations to stress-test your response plans."
- Marsel Fazilov, GRC Security Program Manager, Vanta
Failing to comply with GDPR can result in fines of up to €20 million or 4% of an organization’s annual global turnover, whichever is higher. Regular audits help you catch potential problems early, avoiding costly regulatory penalties or damaging data breaches.
How to Ensure Compliance with Data Protection Regulations
While encryption and access controls are critical for safeguarding data, compliance standards ensure accountability and legal protection. These frameworks outline the rules for handling data responsibly. Ignoring them can lead to hefty fines, so it’s essential to identify which regulations apply to your operations and demonstrate compliance. This legal foundation complements the technical protections discussed in upcoming sections.
Understanding GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 Requirements
When it comes to chatbots, three major compliance frameworks often come into play: GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2.
- GDPR: This regulation applies to any organization processing personal data of EU citizens, no matter where the company is located. GDPR emphasizes principles like data minimization, the "right to be forgotten", and timely breach notifications. Non-compliance can result in penalties reaching as high as €20 million or 4% of annual global revenue, whichever is greater.
- HIPAA: If your chatbot handles Protected Health Information (PHI), HIPAA compliance is non-negotiable. This regulation governs healthcare providers and their Business Associates, including chatbot platform vendors. To comply, you’ll need a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with your provider, and all health data should be anonymized or de-identified to ensure it cannot be traced back to individuals.
"Anonymizing or de-identifying health data before it's processed by ChatGPT can mitigate the risk of PHI breaches. By stripping away identifiable information, the data can no longer be traced back to a specific individual, allowing it to be handled without violating HIPAA regulations."
- Joanne Byron, BS, LPN, CCA, CHA, CHCO, CHBS, CIFHA, CMDP, COCAS, CORCM, OHCC, ICDCT-CM/PCS, American Institute of Healthcare Compliance
- SOC 2 Type 2: This voluntary audit framework is widely adopted by U.S.-based service organizations. It evaluates whether security and confidentiality controls meet industry standards. Unlike GDPR, which enforces strict legal mandates, SOC 2 focuses on demonstrating adherence to privacy commitments through detailed audit reports.
To help meet these requirements, OpenAssistantGPT provides tools like SAML/SSO authentication for secure user access, audit logs to track administrative actions, and data residency options for storing information in specific regions. These features are particularly useful for healthcare or enterprise-focused chatbots.
Maintaining Security Documentation and Audit Logs
Just as encryption and access controls protect data, documentation is what proves these safeguards exist. Compliance isn’t just about implementing measures - it’s about showing evidence. Regulators expect thorough records of security protocols, data handling processes, and incident response plans. For example, HIPAA mandates that compliance-related documentation, including risk analyses and policies, be retained for at least six years.
Start by creating a privacy notice that clearly explains what data is collected, why it’s collected, and how users can access, correct, or delete it. If you’re using a no-code platform, ensure you have a Data Processing Addendum (DPA) in place to outline data handling responsibilities. For healthcare applications, a BAA is also essential.
Audit logs play a key role during compliance reviews. They provide a record of administrative actions, access to sensitive data, and security events like unauthorized access attempts. To avoid accidental exposure, redact any personally identifiable information (PII) from these logs before storing them. OpenAssistantGPT simplifies this process with automated audit log features, ensuring comprehensive tracking and compliance support.
Additionally, data residency controls allow you to store information in specific regions, such as the U.S., Europe, or Japan, to comply with local data sovereignty laws. For applications handling highly sensitive data, consider Zero Data Retention (ZDR) configurations, which exclude customer content from abuse monitoring logs entirely. Together, detailed documentation and robust technical safeguards help establish a strong compliance strategy.
Conclusion
Ensuring the security of no-code chatbots calls for a multi-layered strategy. This includes encryption to protect data during transit, authentication to confirm user identities, regular assessments to identify vulnerabilities, and adherence to compliance frameworks to maintain accountability. Together, these elements form a robust defense system where the failure of one layer is compensated by the strength of others.
At the heart of this approach are a few key principles: granting least privilege access, thoroughly validating inputs and outputs, and treating all external data as inherently untrusted. Permissions should be limited to only what’s absolutely necessary, while user prompts must be sanitized to block injection attacks. Additionally, filtering outputs is critical to prevent sensitive information from being exposed. For high-stakes actions, like financial transactions or data deletion, explicit human approval should always be required.
"Treat every connector as production software: Least privilege, explicit user consent, and defense in depth."
- OpenAI Developers Guide
By applying these principles, you can establish a strong, end-to-end security framework. OpenAssistantGPT integrates these layers seamlessly into its platform, offering features like SOC 2 Type 2 alignment, centralized access management, and SLA guarantees as part of its Enterprise plan. This allows you to focus on building chatbot functionality without the added burden of configuring complex security measures.
Security isn’t a one-and-done task - it’s an ongoing commitment. Regularly monitor for unusual activity, keep detailed documentation, and perform frequent vulnerability checks. Combining these technical safeguards with sound governance and transparency ensures that your chatbots earn and maintain user trust, even when handling sensitive information.
FAQs
What steps can I take to protect no-code chatbots from data breaches?
To keep no-code chatbots safe from data breaches, prioritize encrypting data both while it's being transmitted and when it's stored. Use strong authentication methods, like single sign-on (SSO) combined with multi-factor authentication, and apply role-based access controls to limit user access strictly to what they need. Assign unique identifiers to separate customer data logically, and secure your cloud setup by isolating production and non-production environments.
Make it a habit to audit access permissions regularly, revoke compromised credentials immediately, and maintain strong monitoring systems to spot potential threats early. Also, ensure your chatbot aligns with relevant security standards and frameworks to maintain its integrity and reliability.
How do encryption and authentication protect no-code chatbots from security threats?
Encryption transforms chatbot data into a secure format, ensuring it remains unreadable without the correct key. This process protects sensitive information from being accessed by anyone who isn't authorized.
Authentication, on the other hand, verifies the identity of users or systems interacting with the chatbot. This step ensures that only approved individuals or systems can access or interact with the chatbot.
By combining these two security measures, you can protect sensitive data, block unauthorized access, and preserve the integrity of your chatbot's interactions.
Why are regular security assessments important for keeping chatbots safe?
Regular security assessments play a key role in spotting emerging threats such as prompt injection, privilege escalation, and data leaks. These evaluations confirm whether access controls and least-privilege settings are functioning properly, while also ensuring your chatbot aligns with established security standards.
Consistently reviewing your chatbot’s defenses allows you to address vulnerabilities proactively and protect sensitive information, reinforcing user trust in the process.