How to Prevent OpenAI API Key Leaks

How to Prevent OpenAI API Key Leaks
Your API key is like a password to your OpenAI account. If it gets leaked, it can lead to unexpected charges, data exposure, and service disruption. Protecting it is critical.
Here’s how you can secure your API keys:
- Avoid Hardcoding: Never embed keys in your source code. Use environment variables instead.
- Use Key Management Tools: Services like AWS Secrets Manager and HashiCorp Vault offer secure storage and access controls.
- Limit Access: Assign unique keys to individuals, services, and environments, such as when you build AI Assistant Chatbots. Restrict permissions based on specific needs.
- Rotate Keys Regularly: Replace keys every 60–90 days to minimize exposure risks.
- Monitor Usage: Regularly check for unusual activity in the OpenAI dashboard and set alerts for unexpected spikes.
API Key Security Best Practices
sbb-itb-7a6b5a0
Common Causes of API Key Leaks
To prevent API key leaks, it's essential to first understand how they happen. Here are some common scenarios where API keys are most at risk.
Hardcoding Keys in Source Code
One of the most frequent mistakes is embedding API keys directly into source code. This practice makes keys vulnerable in version control systems like GitHub. If your repository is public, these keys are exposed to the entire world. Even private repositories aren't entirely safe, as they can still be accessed by developers, contractors, or anyone with permissions.
"The biggest problem with storing credentials in source code is that once a credential is in source code it's exposed to any developers who have access to that code, including your version control provider." - Okta Developer
The problem worsens when keys are included in client-side code, such as JavaScript for web browsers or mobile apps. This makes it easy for malicious actors to extract them. Automated bots actively scan public repositories for exposed keys, and a single leak can result in thousands of dollars in unauthorized charges within minutes. It's worth noting that OpenAI typically does not issue refunds for costs incurred due to leaked keys.
Beyond hardcoding, poor access management practices also contribute to key exposure.
Poor Access Controls
Using one API key across an entire team is another common issue. When multiple people rely on the same credential, tracking individual activity or identifying the source of a leak becomes nearly impossible. The problem escalates if the same key is used across development, staging, and production environments, increasing its exposure.
Sharing API keys with third-party tools or services can also be risky. Even well-known libraries or web-based IDEs may not have adequate security measures, putting your keys at risk. Additionally, developers sometimes unintentionally share keys in public forums, email threads, or support tickets, further increasing the chances of exposure.
Accidental Exposure in Logs or Debugging Tools
Verbose logs often capture sensitive information, including headers. Since OpenAI's API keys are transmitted via the Authorization header, they can inadvertently end up in log files or monitoring platforms. Once a key is stored in a centralized logging system, it becomes accessible to anyone with access to those logs, significantly widening the potential damage.
The fallout from a leaked API key goes beyond financial losses. If someone uses your key to generate content that violates OpenAI's terms of service, you, as the account holder, may face consequences. OpenAI disables keys detected on the public internet, but by the time this happens, unauthorized activity could have already drained your quota and racked up charges.
Best Practices for Securing OpenAI API Keys
API Key Storage Methods Comparison: Security Levels and Best Use Cases
Understanding how leaks happen is just the first step. To protect your OpenAI API keys effectively, follow these key practices:
Store API Keys in Environment Variables
Keeping API keys out of your source code is critical, and environment variables are a simple yet effective solution. Instead of embedding keys directly into your application, store them at the operating system level. OpenAI’s SDKs are designed to automatically search for a variable named OPENAI_API_KEY, making this method both secure and easy to implement.
"We recommend that you set the name of the variable to OPENAI_API_KEY. By keeping this variable name consistent across your team, you can commit and share your code without the risk of exposing your API key." - OpenAI
For local development on macOS or Linux, you can add export OPENAI_API_KEY='your_key_here' to your shell profile (like ~/.zshrc or ~/.bash_profile) and activate it by running source ~/.zshrc. On Windows, use the command setx OPENAI_API_KEY "your_key_here" to store it permanently. For production environments, step up your security by building an AI chatbot for your enterprise and integrating key management services.
Use Key Management Services
Key management services such as AWS Secrets Manager, HashiCorp Vault, Azure Key Vault, or Google Secret Manager provide advanced security features like encryption at rest, role-based access controls, and detailed audit logs. These tools centralize your key storage and allow you to monitor who accessed which keys and when.
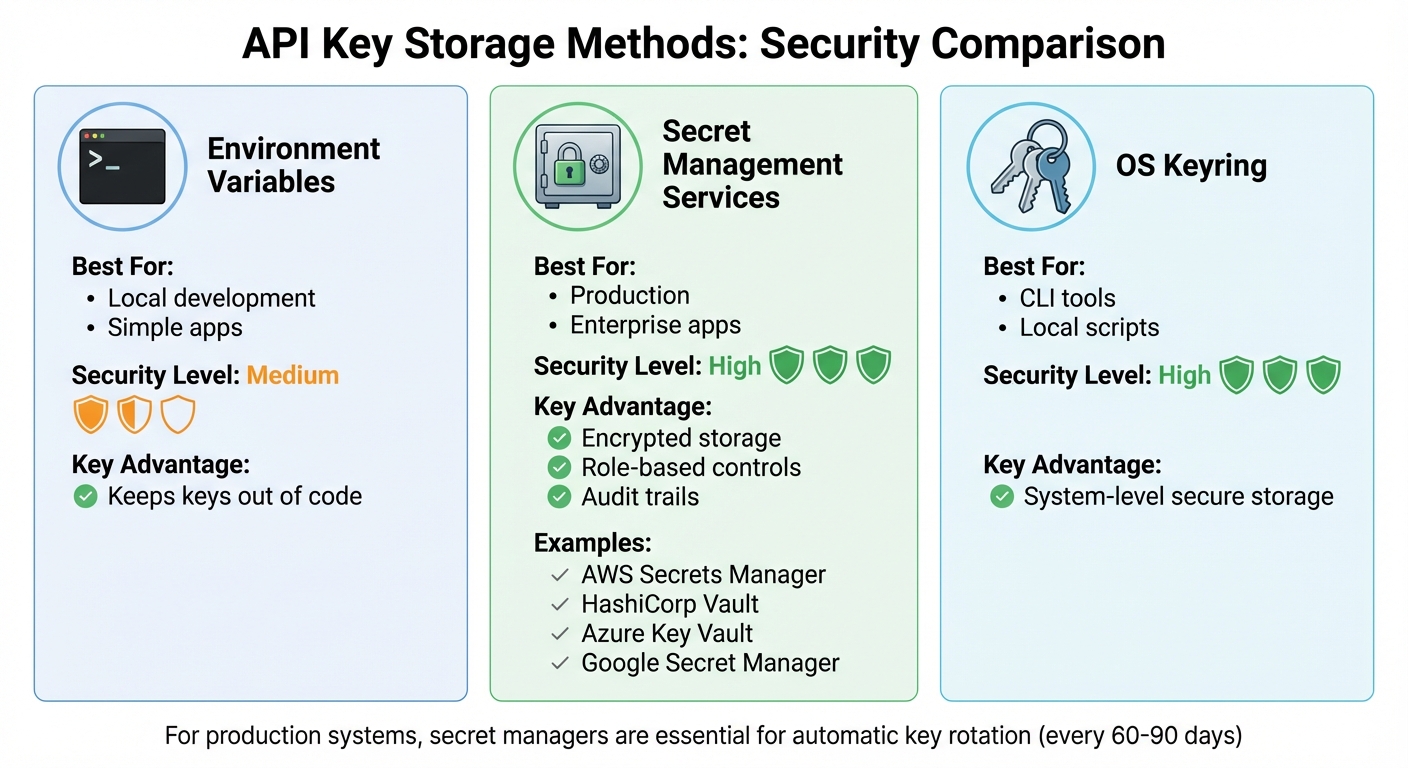
| Storage Method | Best For | Security Level | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environment Variables | Local development / simple apps | Medium | Keeps keys out of code |
| Secret Management Services | Production / enterprise apps | High | Encrypted storage, role-based controls, and audit trails |
| OS Keyring | CLI tools / local scripts | High | System-level secure storage |
For production systems, secret managers are essential. They not only simplify centralized control but also enable automatic key rotation. Many organizations adopt rotation policies where keys are updated every 60–90 days.
Apply Least Privilege Principles
In addition to securely storing your keys, it’s crucial to enforce strict access controls. Avoid sharing a single API key across your team or multiple environments. Instead, assign unique keys to each developer, service, and environment. This approach helps limit potential damage and makes it easier to trace any suspicious activity.
"Consider the least privilege model when deciding on credentials. Separate keys should be used for different services under teams or applications instead of allowing them all to share one master credential." - Reco Security Experts
The OpenAI dashboard allows you to fine-tune each key’s permissions. For example, you can restrict access to expensive models like GPT-4 while enabling GPT-3.5, set request limits per minute, and define spending caps on a daily or monthly basis. OpenAI starts with an approved usage limit of $100 per month once billing information is added. By assigning specific permissions - such as read-only access for certain projects - you can reduce the impact of potential breaches and prevent unauthorized usage from spiraling out of control.
Regular Maintenance and Monitoring Strategies
While secure storage and least privilege controls are key, they’re just the starting point. Protecting your infrastructure over time requires consistent upkeep. Even the best defenses can weaken due to new threats, system exposure, or simple human mistakes. Here’s how to stay ahead and keep your systems secure. If you are building with our platform, refer to our OpenAssistantGPT documentation for specific security configurations.
Rotate API Keys Regularly
Rotating API keys on a regular schedule minimizes the risk of prolonged exposure. It shrinks the window of opportunity for attackers, making it harder for them to exploit compromised keys. Many security teams enforce rotation policies, but the timing should align with your specific risk factors and how widely keys are distributed across your systems.
Using secret management tools like AWS Secrets Manager or HashiCorp Vault can make this process much easier. These tools handle runtime injection of secrets, so you’re not stuck managing keys scattered across your codebase. Avoid injecting secrets at build time - this embeds them in build artifacts, where they can linger indefinitely. Instead, inject secrets at runtime using environment variables.
If you suspect a key has been exposed, act fast: invalidate and replace it immediately. Scheduled rotations are important, but they’re not enough. The longer a compromised key remains active, the greater the potential damage.
Monitor API Usage for Suspicious Activity
Rotating keys is only part of the equation. You also need to keep a close eye on how your APIs are being used. Regularly review the OpenAI dashboard for usage patterns, such as unexpected spikes in activity or unfamiliar interactions.
In production environments, logging is your best friend. Track key details like client IP addresses, user IDs, timestamps, and endpoints to quickly identify unusual behavior. With APIs now accounting for over 83% of internet traffic, and API-related attacks projected to rise by 33% by 2025, proactive monitoring is non-negotiable.
"API security is not optional in a world rife with data breaches and attacks. It's a necessity." - Boomi
Set up automated alerts to flag anomalies, such as repeated failed login attempts, sudden traffic surges, or attempts to access sensitive admin endpoints. Tools that integrate with SIEM systems can correlate API activity with other security events, giving you a broader view of potential threats.
Conduct Code Reviews and Use Automated Scanning Tools
To catch exposed credentials before they cause harm, combine regular code reviews with automated scanning. Tools like Datadog Secret Scanning can identify leaked credentials in your repositories and CI/CD pipelines. Some advanced scanners even verify detected secrets with providers like OpenAI to confirm whether they’re active, helping you focus on real threats while reducing false alarms.
"When a secret is committed to a repository, it spreads quickly across branches, becomes difficult to track, and leads to leaks that are hard to clean up." - Datadog
Adopt pre-commit and pre-merge checks to block changes containing exposed credentials before they’re added to your codebase. This "shift-left" approach addresses issues early, preventing them from spreading. To take it a step further, integrate security testing into your CI/CD pipeline. Standards like OWASP can guide your scans for vulnerabilities, while tools combining Static Code Analysis (SAST), Runtime Code Analysis (IAST), and Software Composition Analysis (SCA) provide thorough coverage throughout your development process.
How OpenAssistantGPT Helps Secure Your OpenAI API Keys
OpenAssistantGPT builds on established security practices to provide extra protection for your OpenAI API keys through a range of integrated tools and features.
Properly managing API keys is essential when working with AI-powered chatbots, and OpenAssistantGPT addresses this by embedding additional safeguards. These measures ensure that even in the event of a key being exposed, potential damage is minimized.
Built-in Tools for Secure Key Management
OpenAssistantGPT employs a two-key system to enhance security by separating administrative tasks from chatbot operations. Here's how it works:
- Global API Key: This key is used for backend operations like uploading files and accessing models.
- Chatbot API Keys: These keys are dedicated solely to generating AI responses, ensuring that any breach is contained to the affected chatbot.
To further protect your setup, the platform encourages using unique API keys for each chatbot. If a key is compromised, you can easily rotate it via the dashboard without disrupting other chatbots. Additionally, automated email alerts notify you instantly if a key becomes disabled, enabling quick responses.
To avoid unexpected costs from malicious activity, OpenAssistantGPT includes throttling options. You can limit usage, such as capping users at 15 messages per day or 5 messages per minute. For internal deployments, Network Security settings allow you to restrict access to specific IP addresses or block unwanted ones.
Custom Authentication for Private Chatbots
For enterprise users looking for stricter security measures, OpenAssistantGPT’s Enterprise plan integrates SAML/SSO authentication with Azure Entra. This ensures only authorized personnel can access private chatbots, reducing the risk of unauthorized API usage. When combined with the two-key system and IP restrictions, these features create a robust defense for your OpenAI API keys.
Conclusion
Keeping your OpenAI API keys secure is a must when it comes to safeguarding your budget, data, and reputation. OpenAI puts it well: "Security is a shared responsibility. While we take all necessary steps to protect your access, following these guidelines will further safeguard your account". While their platform infrastructure is designed to be secure, the responsibility of managing and monitoring your keys lies with you.
A few key practices can make a big difference. Avoid hardcoding your keys - store them in environment variables or use secret managers instead. Always route API requests through a secure backend server rather than exposing keys in browsers or mobile apps. These steps are critical to minimizing risks.
Ongoing maintenance is just as important as setting things up correctly. Security experts suggest rotating your API keys every 60–90 days to limit potential exposure. Additionally, use the OpenAI dashboard to monitor usage and set up notifications for when you hit 90% or 95% of your monthly budget. This can help you catch any unusual activity and prevent billing fraud.
For those looking for a more streamlined approach, OpenAssistantGPT offers tools to simplify secure key management. Features like integrated authentication and SAML/SSO for enterprises reduce the manual effort of implementing security measures while helping to maintain strong protection.
Finally, take a moment to audit your current setup. Add .env files to your .gitignore, enable multi-factor authentication on your OpenAI account, and establish a routine for rotating your keys. These consistent actions will go a long way in building a secure environment for your organization and its users.
FAQs
What’s the best way to keep my OpenAI API keys secure?
To keep your OpenAI API keys safe, here are some key practices to follow:
- Store keys in environment variables: Instead of embedding keys directly in your code, use a
.envfile. Make sure this file is included in your.gitignoreto avoid accidentally sharing it in version control systems. - Leverage secret management tools: For production environments, use services like AWS Secrets Manager, Google Secret Manager, or HashiCorp Vault to securely store and handle your keys.
- Avoid exposing keys in client-side code: Always process API calls through a backend server to ensure your keys stay out of reach from public access.
- Regularly monitor and rotate keys: Change your keys periodically and revoke old ones. Keep track of usage patterns to identify any unusual activity.
Pro Tip: If you're using OpenAssistantGPT to create chatbots, configure your API keys through the platform’s secure settings or a cloud-based secret manager to maintain their security.
Why is hardcoding API keys in my code risky?
Hardcoding API keys directly into your source code is a risky move. If your code gets shared, uploaded to a public repository, or compromised, attackers can quickly extract those keys and misuse them. This could result in unauthorized API access, unexpected costs, or even sensitive data being exposed.
To protect your API keys, store them securely using environment variables or a secret management tool. These methods help keep your keys private and minimize the chances of accidental leaks or breaches.
How often should I rotate my OpenAI API keys to keep them secure?
To keep your systems secure, it's wise to rotate your OpenAI API keys on a regular basis. While OpenAI doesn't mandate a specific rotation schedule, you should align this practice with your organization's security policies and risk management strategies.
For many scenarios, updating keys every few months - or whenever there are changes in team members or shifts in access patterns - can help minimize the chances of unauthorized access.